The State Herbarium of South Australia sits 15 km inland from the nearest sea and houses over one million, mostly dried, specimens. So why are we posting about World Oceans Day?
Despite our terrestrial location, the herbarium is home to significant collections of marine flora (seagrasses) and macroalgae (seaweeds). Not only that, but we are also helmed by seagrass expert and Chief Botanist Michelle Waycott.

FROM THIS: In situ photo of Metamastophora flabellata, being collected by volunteer Fiona McQueen on a collecting trip to Yorke Peninsula. Photo: F. McQueen.

TO THIS: Fiona collecting a part of Sarcomenia delesserioides from Pondalowie Bay to become a herbarium specimen. Photo: F. McQueen.
Treasure trove
The State Herbarium of South Australia is known to contain plant specimens, including the seagrass families, but its world-renowned algal collection may not be common knowledge to the general public. Housed within the herbarium are examples of all 10 South Australian species of seagrass and almost 1300 species of marine macroalgae! This algal species diversity is partly because the seaweeds in the Southern Ocean and its Great Southern Reef have the highest levels of species richness and endemism in the world and partly because of Prof. H.B.S. Womersley’s lifetime work in compiling the six-volume Marine Benthic Flora of Southern Australia with his team at the University of Adelaide and at the State Herbarium.
Of the more than one million specimens in the herbarium, at least 1500 are seagrasses, and close to 100,000 are seaweeds. But don’t mistake these relatively small specimen numbers for insignificance. Quite oppositely, seagrasses and seaweeds are vital to most oceanic functions.

TO HERE: The herbarium’s wet lab where algal specimens are prepared, mounted, studied and identified. Photo: J. Barrett.
Specimens of significance
World Oceans Day is designed to remind people of the importance of the world’s oceans and to encourage them to care enough to engage in marine protection. And so they should. The ocean covers 70% of the planet and supports every other organism. While many factors and organisms are at play, when it comes down to it, the functions of our oceans are very much a product of the plants and algae within:
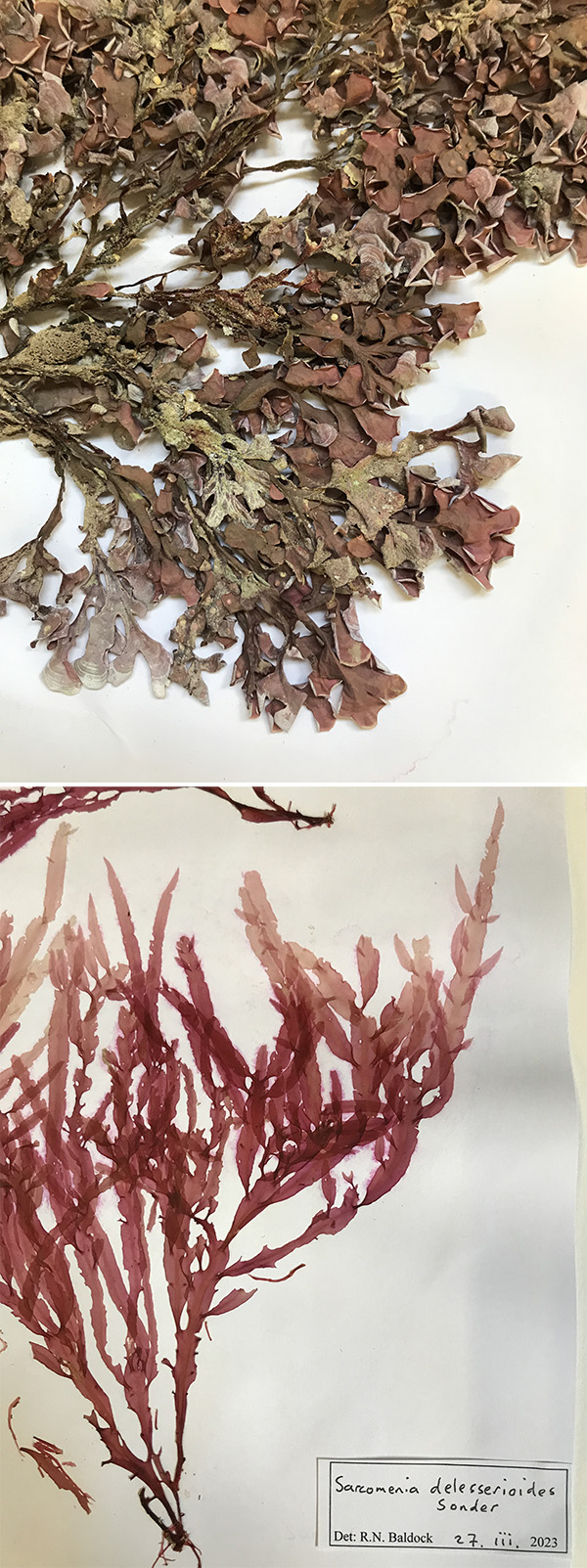

AND FINALLY: The mounted specimens, which were floated onto a preparatory sheet before spending time in the drier and being attached to their final herbarium sheets.
- The vast majority of the planet’s oceanic oxygen is created by microalgae (phytoplankton), macroalgae (seaweeds) and plants (seagrasses). Naturally, photosynthesisers are also effective storers of carbon.
- Not only do the number of seagrass and seaweed species contribute to oceanic diversity, but these species also feed, house and protect countless other marine organisms.
- Both algae and seagrasses are the start of many food chains, nourishing animal groups as diverse as shellfish, crustaceans, birds, fish, marine mammals and even us.
These are but a few blips on the radar of seagrass and seaweed functionality and importance. Unfortunately, our marine ecosystems are in decline. Seagrass meadows are especially in dire straits… and dire gulfs, and dire bays.
A strong foundation
This is where the State Herbarium comes in. Our taxonomical knowledge creates foundational information on species and their distribution, abundance, and history. This provides a baseline of data that allows changes to be noticed and tracked over time.
The specimens in our collection are barcoded and databased. The complete datasets (including species name, collecting location and date, etc.) are sent to the Australasian Virtual Herbarium for broader use by anyone with an interest and Internet access.
Not only does our collection comprise the actual reference specimens, but also a wealth of associated data on species descriptions and locations. When collected and stored over time (the earliest seaweed in our collection is from 1799!) our specimens and data can allow scientists to identify and document change, as well as plan for restoration.
When next June rolls around and World Oceans Day pops into your head, I hope you think of our secret sea of marine specimens housed in The Old Tram Barn (2.7mb PDF) in the middle of an urban capital city, and remember our contribution to ocean conservation and public education.
Compiled by State Herbarium staff member Jem Barrett.
 The State Herbarium of South Australia partnered with the Pastoral Unit (Department for Environment and Water), to produce this new second edition, which was revised by Tim Croft and Jürgen Kellermann from the State Herbarium. It has been completely reformatted and newly type-set, all plant names have been updated, descriptions were revised, photos were added or replaced with better images. Ten more species were added to the book.
The State Herbarium of South Australia partnered with the Pastoral Unit (Department for Environment and Water), to produce this new second edition, which was revised by Tim Croft and Jürgen Kellermann from the State Herbarium. It has been completely reformatted and newly type-set, all plant names have been updated, descriptions were revised, photos were added or replaced with better images. Ten more species were added to the book.



 Among this year’s recipients was
Among this year’s recipients was 





You must be logged in to post a comment.